Difference between revisions of "WebSky Extragalactic CMB Mocks"
(username removed) (edit summary removed) |
(→Data: adding comment pointing to where the sims are saved) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <gallery mode=packed heights=" | + | <gallery mode="packed-hover" heights="300px"> |
| − | File: | + | File:montage.png | [[Media:montage.png|Websky maps]] |
| − | + | File:Lightcone_60arcmin_300dpi.png | [[Media:Lightcone_60arcmin_300dpi.png | Websky halos ]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
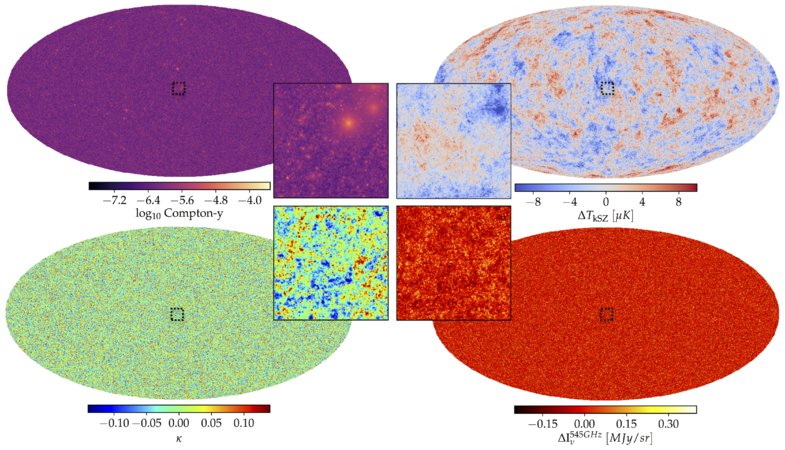
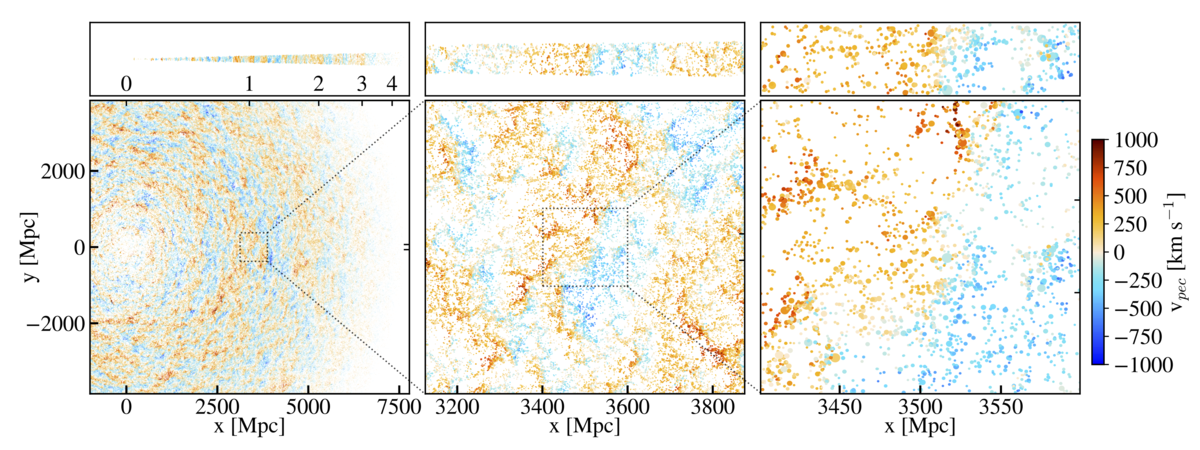
| − | + | Provided are [https://healpix.jpl.nasa.gov/ HEALPix] .fits files over the full sky at nside=4096 of CIB (in MJy/sr) intensity, Compton-y, kSZ (mu K), CMB lensing convergence, and lensed and un-lensed CMB TT, EE, and BB maps, all from the same 12288^3 particle, 15.4 Gpc peak-patch and 2LPT based cosmological simulation, as well as the light cone halo catalog itself. The minimum halo mass used was ~1.4e12 M200,M. Higher resolution maps and different frequencies are available upon request. For a full description of the contents of these maps see ''The Websky Extragalactic CMB Simulations'' - https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08787. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | = Data = | |
| − | + | Data, including [http://mocks.cita.utoronto.ca/data/websky/v0.0 README], available [http://mocks.cita.utoronto.ca/data/websky/v0.0 here] | |
| − | + | <!-- Note that the WebSky simulation products can be found on CITA servers at /fs/lustre/project/act/mocks/websky/v0.0/ --> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | = Figures = | ||
| + | <gallery mode="packed-hover" heights="250px"> | ||
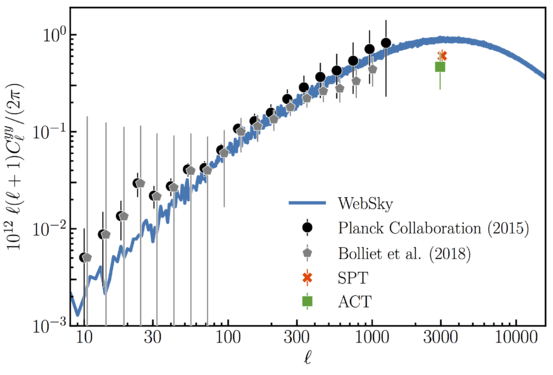
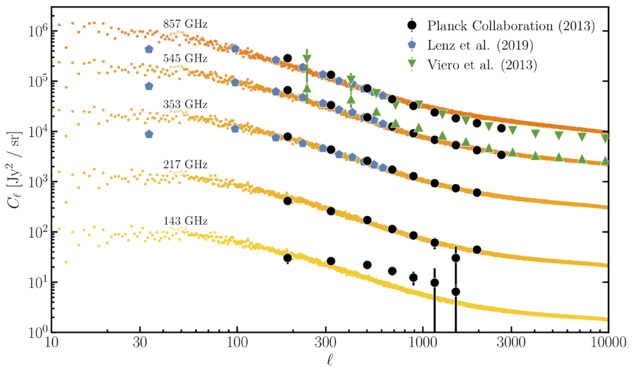
| + | File:tsz.png | [[Media:tsz.png | tSZ power spectrum ]] | ||
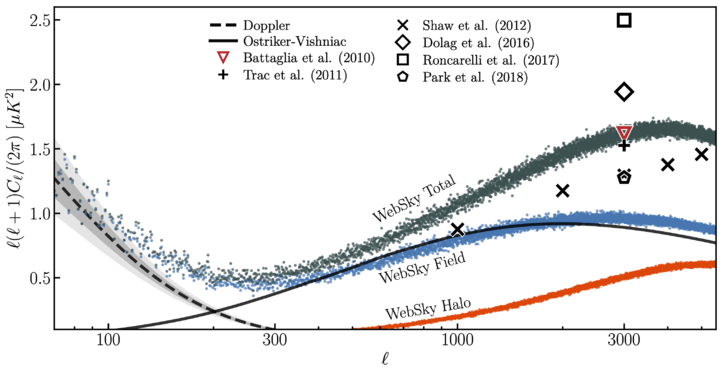
| + | File:ksz.png | [[Media:ksz.png | kSZ power spectrum ]] | ||
| + | File:cib.png | [[Media:cib.png | CIB power spectra ]] | ||
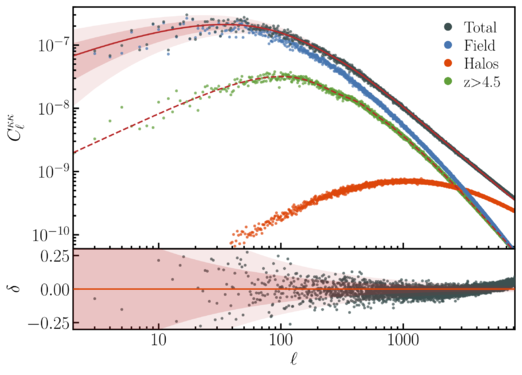
| + | File:KappaPower.png | [[Media:KappaPower.png | Convergence power spectrum ]] | ||
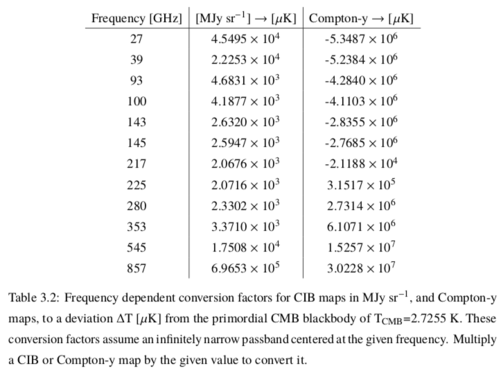
| + | File:conversion_factors.png | [[Media:conversion_factors.png | Conversion factors from native maps to delta Tcmb]] | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | = | + | = Acknowledgments = |
| − | + | The WebSky Extragalactic CMB Mocks Collaboration consists of George Stein, Marcelo Alvarez, Dick Bond, Alex van Engelen, Nick Battaglia, and Zack Li, with additional contributions from Amir Hajian. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In order to properly acknowledge our efforts, we request the following paragraph to be included in the “Acknowledgements” section of any publication | |
| − | + | which makes use of the simulation data above, and ask you to cite the following papers: | |
| − | + | Paper 2: ''The Websky Extragalactic CMB Simulations'' - G. Stein, M. A. Alvarez, J. R. Bond, A. v. Engelen, N. Battaglia (2020). https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08787 | |
| − | The | ||
| − | + | Paper 1: ''The mass-Peak Patch algorithm for fast generation of deep all-sky dark matter halo catalogues and its N-Body validation'' - G. Stein, M. A. Alvarez, J. R. Bond (2019). https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.07727 | |
| − | |||
| − | "The sky simulations used in this paper were developed by the WebSky Extragalactic CMB Mocks team, with the continuous support of the Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics (CITA), the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR), and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (NSERC), and were generated on the | + | "The sky simulations used in this paper were developed by the WebSky Extragalactic CMB Mocks team, with the continuous support of the Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics (CITA), the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR), and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (NSERC), and were generated on the Niagara supercomputer at the SciNet HPC Consortium (cite https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.13600). SciNet is funded by: the Canada Foundation for Innovation under the auspices of Compute Canada; the Government of Ontario; Ontario Research Fund - Research Excellence; and the University of Toronto." |
| − | [[ Internal Pages ]] | + | [[ Documentation | Internal Pages ]] |
Latest revision as of 18:36, 14 August 2024
Provided are HEALPix .fits files over the full sky at nside=4096 of CIB (in MJy/sr) intensity, Compton-y, kSZ (mu K), CMB lensing convergence, and lensed and un-lensed CMB TT, EE, and BB maps, all from the same 12288^3 particle, 15.4 Gpc peak-patch and 2LPT based cosmological simulation, as well as the light cone halo catalog itself. The minimum halo mass used was ~1.4e12 M200,M. Higher resolution maps and different frequencies are available upon request. For a full description of the contents of these maps see The Websky Extragalactic CMB Simulations - https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08787.
Data
Data, including README, available here
Figures
Acknowledgments
The WebSky Extragalactic CMB Mocks Collaboration consists of George Stein, Marcelo Alvarez, Dick Bond, Alex van Engelen, Nick Battaglia, and Zack Li, with additional contributions from Amir Hajian.
In order to properly acknowledge our efforts, we request the following paragraph to be included in the “Acknowledgements” section of any publication which makes use of the simulation data above, and ask you to cite the following papers:
Paper 2: The Websky Extragalactic CMB Simulations - G. Stein, M. A. Alvarez, J. R. Bond, A. v. Engelen, N. Battaglia (2020). https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08787
Paper 1: The mass-Peak Patch algorithm for fast generation of deep all-sky dark matter halo catalogues and its N-Body validation - G. Stein, M. A. Alvarez, J. R. Bond (2019). https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.07727
"The sky simulations used in this paper were developed by the WebSky Extragalactic CMB Mocks team, with the continuous support of the Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics (CITA), the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR), and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (NSERC), and were generated on the Niagara supercomputer at the SciNet HPC Consortium (cite https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.13600). SciNet is funded by: the Canada Foundation for Innovation under the auspices of Compute Canada; the Government of Ontario; Ontario Research Fund - Research Excellence; and the University of Toronto."